Contents
Key Insights
Core Investment Logic
Anyswap is a decentralized cross-chain exchange protocol that focuses on cross-chain bridge services and asset cross-chain business. As new public chains sprung up under blockchain business blowout in 2021, its cross-chain business saw a spring in its step. Among all the third-party cross-chain bridges that have gone live, Anyswap is way ahead of its peers in terms of business data across multiple dimensions, thanks to the following advantages:
- The project has launched its products early, thus gaining high recognition.
- DCRM-based cross-chain solution for assets can be applied to all public chain platforms that boast Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA), with lower technical and development costs, more efficient deployment and connection, and faster public chain integration.
- Newer public chains tend to cooperate with the most well-known cross-chain bridges that support the most public chains, are best funded (great cross-chain depth), and have the largest user base, further strengthening Anyswap’s competitive advantages with decent network effects.
While fast-growing new public chains have created a huge demand for asset cross-chains, their contraction will lead to a direct shrinkage in the market size of asset cross-chains. This means that the Anyswap project is closely related to the public chain market landscape.
Main Risks
Potential risks for Anyswap include node centrality, contraction of new public chains, traffic and fee stranglehold by cross-chain aggregators on individual cross-chain platforms, code vulnerabilities and hacking, as described in Risks.
Valuation
PE and PS were measured on Anyswap’s fully diluted and liquid market capitalization, and the former stood in the mid-range of mainstream DeFi projects.
Project Information
Business Scope
Anyswap is a decentralized asset cross-chain bridge that concentrates on asset cross-chain, incubated and developed by core members of the public chain project Fusion. Anyswap used to include a transaction function, but later focused its business on asset cross-chain and removed the dex function. Compared with other cross-chain bridges that have been launched so far, it now supports up to 25 chains, including 22 EVM chains, the richest variety of public chains.
Milestones and Roadmaps
| Time | Events |
| 7/12/2020 | The team announced the launch date, introduced the product structure, and disclosed the token allocation protocol. |
| 7/20/2020 | Anyswap was officially launched. |
| 9/14/2020 | The BSC version was launched, and the team offered 500 million ANY as an initial liquidity and trading bonus. |
| 9/17/2020 | Anyswap announced the airdrop of ANY tokens for Uniswap’s 40,000+ liquidity providers and 250,000+ addresses that receive air-dropped Uni tokens. |
| 9/30/2020 | Anyswap announced integration with the Bitcoin mainnet and support for BTC’s assets across the chain. |
| 10/21/2020 | Anyswap announced support for a new batch of cross-chain assets, including LINK, DAI, YFI, COMP and OMG. |
| 10/22/2020 | Anyswap was included with Pancakeswap and Bakeryswap in the first 6 projects to receive awards from the Binance Smart Chain Accelerator Fund. |
| 11/11/2020 | Fantom version was launched to support FTM, wFTM, ETH, USDT, YFI, FSN and ANY, while liquidity bonus for FTM trading pairs was initiated. |
| 11/18/2020 | The Ethernet version was launched, marking the first liquidity mining of Ethernet network assets. |
| 12/8/2020 | Anyswap announced integration with the Litecoin mainnet and support for asset cross-chaining of Litecoin, as well as liquidity mining for LTC on FSN, Ether, BSC and Fantom. |
| 12/22/2020 | Anyswap updated Heco version. |
| 1/2021 | Anyswap kicked off a liquidity mining incentive campaign for the Fusion and Fantom main chains. |
| 2/2021 | Anyswap suspended ANY incentive for liquidity mining in the AMM mechanism, and removed the trading function to focus on asset cross-chain business. |
| 3/22/2021 | Anyswap announced a deep collaboration with Sushiswap on direct cross-chain transactions. |
| 3/22/2021 | Anyswap announced the launch of Polygon version. |
| 3/25/2021 | Anyswap announced the launch of xDAI version. |
| 4/14/2021 | Anyswap announced the launch of Avalanche version. |
| 6/3/2021 | Anyswap announced its first token destruction, repurchasing 160,485 tokens with cross-chain fees incurred in April.ANY tokens, representing 0.9% of the volume in circulation at the time. |
| 6/4/2021 | The V3 protocol was launched and first deployed on BSC, Fantom and Polygon.V3 is characterized by cross-chain protocols for non-escrow and multi-party secure computing, native asset (i.e., non-wrapped asset) transactions, and multi-chain routing. |
| 6/2021 | V3 enabled liquidity mining for both Polygon and Fantom chains. |
| 7/10/2021 | V3 was hacked, costing Anyswap about $7.9 million, and Anyswap subsequently fixed the bug and took full responsibility for the loss. |
| 7/20/2021 | Anyswap announced the launch of the Kucoin public chain. |
| 7/30/2021 | Anyswap announced the launch of Okexchain. |
| 8/31/2021 | Anyswap announced a partnership with Boba and completed deployment on the Boba test network, with the official version to follow. |
| 9/8/2021 | Anyswap has entered into a partnership with Harmony to launch the Harmony version. |
| 9/15/2021 | Anyswap was equipped with the V3-based NFT cross-chain bridge feature (Alpha test version), supporting cross-chain testing of ERC721 and ERC1155 format NFT between Ethereum and Fantom.Anyswap was equipped with the V3-based NFT cross-chain bridge feature (Alpha test version), supporting cross-chain testing of ERC721 and ERC1155 format NFT between Ethereum and Fantom. |
| 9/23/2021 | Anyswap announced the launch of Moonriver version. |
| 9/28/2021 | Anyswap announced the launch of lotex version. |
| 10/15/2021 | Anyswap announced the launch of Shiden version. |
| 11/8/2021 | Anyswap implemented a second ANY repurchase and destruction, destroying 115,542 ANY tokens, worth $1.38 million at the time. |
| 11/19/2021 | Anyswap announced the launch of Telos version. |
| 12/2/2021 | Anyswap announced support for Terra’s stablecoin asset UST cross-chain between Terra mainnet and Fantom mainnet. |
| 12/4/2021 | Binance supported the Anyswap (ANY) token. |
Business Details
Business Logic
After February 2021, Anyswap shifted its main business from asset cross-chain + transaction to asset cross-chain. Also, Anyswap designs two cross-chain solutions, called V2 and V3 versions.
V2
Both V2 and V3 solutions rely on Anyswap’s DCRM+TSS program that fits all ECDSA-based public chain platforms, making them very easy to deploy cross-chain services.
DCRM or Distributed Control Rights Management is designed and developed by the Fusion team based on the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) and the Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS).
TSS is a type of digital signature protocol used by Mutli-party Computation (MPC) wallets to sign for mobilizing user assets in escrow accounts. In this signature protocol, multiple parties are allowed to jointly generate keys and signatures, but no party has its own full key or sign away assets without the consent of the other parties.
Cross-chain process in Anyswap documentation, source from: https://anyswap-faq.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html
According to V2 solution, cross-chain is performed in 1-to-1 mint/burn model. Specifically, the user will deposit the assets to be cross-chained into the escrow address managed by DCRM, then the assets on the original chain will be locked by the signature node selected by Anyswap based on the TSS signature protocol, and the wrapped asset Anytoken (such as AnyUSDT) of the original chain assets will be minted on the target chain, similar to the encapsulation of BTC as WBTC.
When the user redeems the wrapped assets, the wrapped assets on the target chain are destroyed, and the assets locked on the original chain are released to the user.
Cross-chain in V2 solution: the user gets USDT wrapped by Anyswap through cross-chain; Source: https://anyswap.exchange/#/bridge
V3
V3 is a many-to-many model that allows for native assets on multiple cooperating chains. The native assets include BEP20 and ERC20 tokens minted by the project parties in addition to the main chain tokens such as BNB/ETH.
As an example, a project has project tokens A on both BSC and ETH, but they are in the format of BEP20 and ERC20, respectively, both of which are officially issued / minted. Then under V3, if a user holding token A wants to cross-chain token A from BSC to ETH, and token A has a sufficient reserve in the pool on Anyswap’s main ethernet, the user can directly exchange for the ERC20 version of the native tokens instead of the tokens wrapped by Anyswap.
Cross-chain in V3 solution: the user gets native assets rather than wrapped assets, and can see the size of the pool across chains; Source: https://anyswap.exchange/#/router
In addition to enabling direct cross-chaining of native assets, V3 has two additional features over V2: non-custodial and multi-chain routing.
Non-custodial: Cross-chain assets are stored on accounts controlled by multi-signatory nodes in V2, while assets are locked in a smart contract in V3, so that only the user can control the assets in the contract unless the nodes collectively violate the contract or there is a problem with contract security.
Multi-chain routing: With a more concise design whereby “users deposit assets in the A-chain pool and get the corresponding assets in the B-chain pool”, multi-chain routing eliminates the cumbersome process of V2 solution by establishing native token pools on multiple deployed chains, thus reducing the cost of Gas.
On Anyswap product interface, V3 and V2 coexist, with two separate portals.
Anyswap defaults to V2 when the user selects “cross-chain bridge”, and V3 when the user clicks “cross-chain routing”.
Signature Nodes
In the cross-chain process, Anyswap MPC nodes are responsible for verifying messages and performing signatures to process cross-chains and transfers. Anyswap currently has 34 MPC nodes, which are expected to be maintained by the official team, but 0 node is pledged as shown on the interface. There is no update yet on node opening and the MPC rules, and the specific time of opening and pledging is unknown.
Source: https://anyswap.net/network
Business Data
According to Anyswap’s official disclosure, its core business data are as follows:
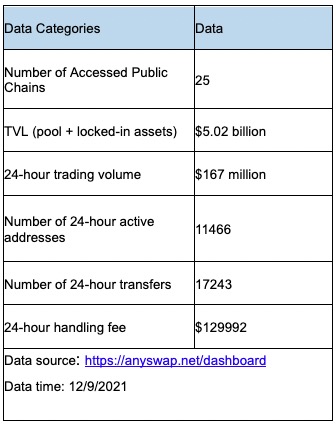
Anyswap, as a third-party asset cross-chain platform, is the absolute leader among current asset cross-chain projects in terms of the number of supported public chains, the amount of locked-in funds (which can be interpreted as the depth of cross-chain funds) and the volume of active users.
Based on the same data dimensions, cBridge, a third-party asset cross-chain bridge in the first tier, and Polygon’s PoS cross-chain bridge were compared to Anyswap.
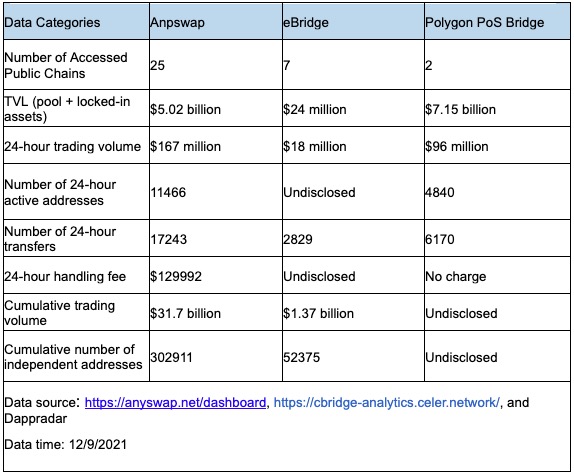
Anyswap is much ahead of its third-party cross-chain bridge rivals in several data dimensions, even surpassing the official cross-chain bridges for new public chains in the first tier according to total cross-chain data for multiple chains.
Besides, Anyswap is becoming the designated or recommended cross-chain bridge for many new public chains, effectively playing the role of the official cross-chain bridge.
For example, on the official page of Fantom, Anyswap is the recommended cross-chain bridge.
Source: https://fantom.foundation/
BSC, the new public chain with the largest number of users at present, has recently shut down its once official cross-chain bridge, Binance Bridge, and has listed Anyswap and cBridge as its cross-chain platforms in addition to recommending users to use Binance CEX as a cross-chain transit. In fact, Anyswap is currently the cross-chain platform with the highest TVL on BSC.
Source: https://www.binance.org/en/bridge
This also happens in disguise with other newer and ecologically smaller public chain projects. Anyswap is also the cross-chain platform with the highest TVL on Moonriver and actually plays the role of the official bridge.
In the landscape of one super-powerful and many powerful public chains, how to attract enough users, funds and developers to their ecology is the most critical issue for newer and smaller public chains. Cross-chain bridge is the only channel to bring funds from other public chains into their own ecology.
At this point, the public chain is faced with 3 options.
- Build cross-chain bridges to connect with other chains;
- Use the leading third-party cross-chain bridge currently available on the market as a cross-chain protocol; and
- Implement 1 and 2 at concurrently.
Since Anyswap holds a safe lead in the number of supported public chains, total funding (cross-chain depth) and user size, it is likely to be the first option for new public chains in the 2 or 3 protocol.
This is confirmed in the interviews with Anyswap partners. Anyswap is known to be very busy, with 5-6 public chain projects in the queue, and it will prefer those with “better user base and ecology”.
The integration of more quality new public chains in turn strengthens Anyswap’s advantage in public chain count, total funding and user scale, creating a virtuous circle that continues to expand its lead in the third-party cross-chain field.
Public chains and tokens that Anyswap has integrated, source: Anyswap twitter
Team
Binance and Andre Cronje are noteworthy partners of Anyswap.
BSC gave Anyswap and five other projects including Pancakeswap and Bakeryswap a $1 billion grant each in October 2020, as part of its accelerator program.
Anyswap is also one of the two decentralized cross-chain platforms officially recommended by Binance after the Binance Bridge went offline.
Andre Cronje, one of the most well-known KOLs and eco-leaders in the crypto world, has played a huge role in the development of AnySwap. He is deeply involved in the development and auditing of the Anyswap cross-chain bridge and multichain cross-chain bridge applications, while Anyswap acts as the core cross-chain bridge in the Fantom ecosystem, a public chain that he strongly supports. On the application side, the stablecoin lending project Abracadabra also integrates Anyswap.
Business Analysis
Industry Space and Potential
Cross-chain Bridge
Anyswap is in the cross-chain bridge infrastructure.
Before introducing a cross-chain bridge, it is necessary to define it. For most users, the cross-chain bridge mainly functions to enable the transfer of assets between multiple public chains, but the transfer is only one of its functions at a broad level. In the abstract, a cross-chain bridge is a system for transferring information between two or more blockchains, where “information” includes not only assets, but also protocol calls, proofs or states.
According to Dmitriy Berenzon, a research partner at 1kx Fund, once summarized that a cross-chain bridge will, in general, contain the following functional modules:
a. Message Monitoring
This module is responsible for monitoring the information in the corresponding chain, generally comprising an Actor, a prophet, and a verifier to monitor the state of the chain.
b. Messaging
After receiving the target event, the module passes it to another chain.
c. Message Consensus
In some cross-chain bridge systems, consensus needs to be reached between the participant nodes on the monitoring chain and passed to another chain, such as Polygon’s POS chain and Celer’s cBridge.
d. Message Signature
The monitor /Actor/ participant node needs to sign the message sent to another chain to perform a cross-chain operation.
Asset cross-chaining is still the most easily perceived business that directly brings cash flow and users to a cross-chain bridge project. Therefore, this report focuses on Anyswap’s main business, asset cross-chain, and does not yet include the broader message cross-chain business.
Although cross-chain business and cross-chain bridge applications were discussed and practiced several years ago, decentralized cross-chain bridge business exploded in 2021. And the explosion occurred amid the rise of crypto commerce from 2020 to 2021.
Within two years, blockchain business has experienced the booming of multiple tracks, such as DeFi in summer 2020, NFT in spring 2021, chain tour in the second half of 2021 and the recent crypto social platform, and officially started to transition from pure concept hype to the era of product and business operation, which can be called the “first year” of blockchain business.
This rapid development has brought about a surge in capital, population and computing demand, which directly pushed up the price of Ethereum Gas. A large number of new public chains with low cost and EVM compatibility have emerged to absorb the overflow traffic from Ethereum. Various decentralized commercial applications are gradually blossoming in multiple chains, so that crypto users who were once loyal to Ethereum have started their “multi-chain nomadic” journey. As a result, the spring of cross-chain bridges has arrived.
In the long term, a cross-chain bridge is necessary in three aspects:
- Improve the utilization and utility of assets
The best case in point is the introduction of BTC into Ether as a key asset for DeFi. Each public chain and its core assets has its fans and community, but even those Bitcoin maximalists would be happy to see more application scenarios and liquidity for Bitcoin on other public chains, such as as collateral for the loan of other assets, or as market-making funds to get revenue from transaction fees, and as a means of payment for consumer goods like services and NFTs. Cross-chain bridges offer a wider range of application scenarios for assets, improve asset utilization, and provide significant added value to users.
Chart of BTC minted on Ether, data source: https://dune.xyz/queries/4962/9776
- Expand the market boundaries of existing protocols and the possibility of developing new features
Through cross-chain bridging, existing protocol products further expand the scope of their services and provide richer services based on multi-chain capabilities to enhance the competitiveness of their protocols and offer better services to users. This trend is reflected in the V3 product program launched by the well-known cryptocurrency protocol Aave, of which cross-chain is the most exciting feature.
On the one hand, Aave will expand its service range (it is currently deployed on three chains, Ether, Polygon and Avalanche) through cross-chain functionality to new public chains such as Solana, Fantom and Harmony, as well as layer 2 networks like Starknet and Arbitrum.
On the other hand, Aave will provide more competitive services and a cohesive community based on its cross-chain features, such as seamless transfer and lending of funds between multiple chains and support for voting governance of multiple chains.
In the long run, supporting multi-chain services will become the mainstream and standard for dApp.
Multi-chain planning in the Aave V3 article; Image source: https://governance.aave.com/t/introducing-aave-v3/6035
- Provide more options for users and developers
Through cross-chain bridges, users and engineers can find more ways:
– Quickly capture arbitrage opportunities that exist only between multiple chains, such as asset and interest rate spreads between multiple trading or lending markets
– Distribute and leverage NFT based on multi-chain (Anyswap already practiced it)
In a multi-chain landscape, cross-chain bridges are essential infrastructure for users, engineers, protocol parties, and even the public chain itself. Unlike most users’ perception of cross-chain bridges as an “application”, they are closer to a prophecy machine, a data index, and an important “middleware” in the multi-chain ecosystem.
Industry Size and Growth
Cross-chain bridges are in great diversity, spanning from official products operated by various public chains, such as the Polygon POS between Polygon and Ether, and Wormhole developed by Solana, to Anyswap and cBrigde, among other comprehensive products developed and operated by third parties.
The data for each cross-chain bridge is not fully disclosed, so it is harder to get a global count, but the TVL growth of cross-chain bridges on Ethereum provides a glimpse of the industry size and growth.
According to @eliasimos on Duneanalytics, the TVL of major cross-chain bridges on Ethereum has exploded since March-April 2021 and experienced a jump in October, with total TVL now at about $24.5 billion. Ronin bridge (Axie’s sidechain), Avalanche bridge and Polygon bridge are in the top three TVLs, with $6.9 billion, $6.6 billion and $5.5 billion respectively (5 Dec 2021 data).
And the number of independent addresses that have access interactions with the cross-chain bridge reached 125,000 in 30 days.
TVL of cross-chain bridges on Ethereum; Data source: https://dune.xyz/eliasimos/Bridge-Away-(from-Ethereum)
The year 2021 undoubtedly witnessed an explosion of cross-chain bridges. In terms of growth rate, the TVL of Ethereum cross-chain bridges has grown from about $600 million in mid-April to $24.5 billion, topping out at $25 billion, an increase of over 4,000% in six months. Going forward, if multiple chains continue to maintain its current landscape where each chain carries out a mixed polymorphic development, the cross-chain bridge will share the industry growth rate, and even get a higher growth rate than the crypto industry.
Competition Landscape
Multi-chain concurrency was not favored by most people until the wave of blockchain business that boomed in 2020 and culminated in 2021, when the overflow of funds and users from Ethereum allowed many new public chains to rise rapidly. Consequently, the demand for assets across chains matured, making this business, which originally seemed like a chicken feed, popular.
The public chains rose so suddenly that few cross-chain bridges were launched for decentralized assets or matured, most of which were official and Ethereum cross-chain bridges built by public chains themselves. These cross-chain bridges were more of a tool for their own ecosystem, and their urge to expand and compete was far less than that of “wild” third-party cross-chain bridges across Anyswap, cBridge and Hop.
Among third-party cross-chain bridges, Anyswap puts itself in the lead with three advantages.
- It was laid out and launched earlier, so it is more popular.
- Its DCRM-based cross-chain protocol for assets can be applied to all ECDSA-equipped public chain platforms, with lower technical and development costs and higher deployment and interfacing efficiency.
- New public chains tend to cooperate with the cross-chain bridge with the most supported public chains, the largest amount of funding (good cross-chain depth), the largest volume of users and the highest popularity, strengthening Anyswap’s competitive advantage and giving it a network effect.
These advantages are demonstrated by Anyswap’s business data, which makes it far ahead in the total number of supported public chains, lockup funds (liquidity) and user volume, as detailed in Business Data.
Nonetheless, the advantages are not enough to rest on its laurels, as it may be exposed to the following potential threats:
- Other cross-chain bridges have replicated its cross-chain deployment protocols or developed more user-friendly protocols, while leveraging token subsidies to close the gap in cross-chain liquidity.
- After the public chain war comes to an end, many new public chains will die, and multi-chain development will shrink, leaving competitive public chains in the single digits. Therefore, Anyswap’s advantage in “supporting a large number of public chains” is weakened.
- Cross-chain aggregator players swarm into Li.finance and Xy.finance, becoming Anyswap’s upstream, diverting its traffic, and thinning its ability to charge for cross-chain business.
Token Analysis
Anyswap uses a single coin model with only one token: Any. Over the year since the project went live, the token model has been tweaked several times.
Token Volume and Release Protocol
Any tokens total 100 million, and without pre-sales or funding, they are initially distributed as follows:
| Assignee | Proportion | Usage |
| Community Ecology Fund | 10% | Managed by the team for project operations and growth |
| Initial Liquidity | 5% | Placed in Anyswap’s flow pool as initial liquidity |
| Used as DCRM cross-chain node rewards | 10% | To incentivize the continuous and stable operation of cross-chain verification nodes |
| Market Maker Incentive | 15% | Given to market makers providing liquidity to trading pairs in Anyswap |
| Team Awards | 15% | As an incentive for current and future teams |
| Company Shareholders | 20% | Shareholders attributed to Anyswap |
| Trading Bonus | 25% | Used for motivating Anyswap traders |
However, the tokens were not allocated exactly as designed, due to the removal of the trading function, and the absence of the node campaign mechanism.
According to the announcement made on October 22, 2021, the total actual supply of Any in circulation as of that time was 18,639,320, a figure that has not increased since February 2021.
Anyswap’s token circulation and distribution across chains as of October 22, 2021
The remaining 80 million or so uncirculated Any tokens will be locked within a smart contract, with governance voting on how they are used in the future.
Token Uses and Scenarios
The Any token was originally designed for the following scenarios:
- Voting for supported master chains
- Voting for working nodes across chains
- Voting for governance rules
In other words, Any at that time was a pure governance token.
However, the constantly expanding business made continuous access to the main chain a “must”, for which the vote became meaningless. Furthermore, the cross-chain node campaign was never detailed, so Any became increasingly invisible in the project.
Beginning in February 2021, Anyswap announced that it will use 20% of the cross-chain business fees to repurchase and destroy Any tokens, going into deflationary mode until the repurchase reaches 30% of the total.
Anyswap’s rates:
If the user chooses Bridge (V2) cross-chain protocol, then
- There is no charge for tokens except for ETH which will be charged at 0.1%, when deposited across chains.
- 0.1% fee will be charged for taking out assets across chains, a minimum fee of at least $5 for other tokens, at least $80 for ethereum, a maximum fee of $1000 for a single coin
If the user goes multi-chain routing protocol (V3), then
- Stablecoin that are transferred to BSC, Fantom, Polygon, and OkExChain across chains will be charged at $0.9 per receipt
- Other tokens will be charged at 0.1% per receipt, corresponding to the different minimum and maximum fees
Summary
Any, the core token of the project, is primarily to capture the 20% fee charged by the protocol through repurchase and destruction and may be subsequently used for pledging and voting in node campaigns.
Risks
Anyswap faces four risks as below:
Centralized Nodes with Too Much Power
The cross-chain multi-signature consisting of MPC nodes does not introduce voting and collateral mechanisms, making the nodes highly centralized. However, decentralization is the way to go, as the assets within the Anyswap protocol continue to expand.
But even with a node-collateralization mechanism, the market value of Any tokens in circulation is a significant distance from the total capital value within its protocol, creating an asymmetry between secured and controlled capital. Discus Fish had implicitly expressed his concern about this. Therefore, it is worthwhile to restrain the joint perpetration of nodes through a good node mechanism.
Code Vulnerabilities and Hacking Attacks
In July 2021, V3 solution was attacked, and about $7.9 million in assets were stolen, although the AnySwap team has recreated the hack’s modus operandi. According to the post-mortem review, two transactions were signed by the same account on the BSC chain. If the transactions had the same r value of rsv signature, the hacker could deduce the private key of the account in reverse. As the protocol funding continues to expand, Anyswap will remain a focus of interest for hackers.
Cross-chain Demand will Shrink After New Public Chains Ebb
The demand for assets across chains generates from the business ecology of multiple chains. However, Anyswap’s advantage in supporting massive public chains will be weakened, if Ethereum receives a performance boost, and the public chain pattern is solid with one superpower and many powers, leaving few opportunities for small public chains.
Growing Cross-link Aggregators Intercept Project Traffic and Suppress the Bargaining of Project Fees
Cross-chain aggregators provide the best-priced cross-chain protocol for users with cross-chain asset needs, which may pool traffic to the aggregator instead of using Anyswap directly (as if many users have become accustomed to using 1 inch instead of a specific DEX for transactions). As the aggregators will choose the path with the lowest loss after comparing multiple cross-chain platforms on the market, only the cross-chain platform with the lowest fees will be able to match the transactions of aggregator users.
Once cross-chain aggregators are accepted by most users, platforms may get into a “fee war” and lose bargaining power.
Preliminary Value Assessment
Five Core Issues
What Business Cycle is the Project in? Is it in Maturity or the Early to Mid-stage?
The year 2021 saw the explosion of the multi-chain ecology and the adolescence of cross-chain platforms.
Anyswap was in the early to mid-stage of development, although the demand for multi-chain interconnection was expected to grow further with the blockchain business.
Does the Project Have Solid Competitive Advantages? What are the Competitive Advantages?
Anyswap is currently the leading third-party cross-chain bridge, with the following competitive advantages:
- It was launched earlier, so it is more popular
- Its DCRM-based cross-chain protocol for assets can be applied to all ECDSA-equipped public chain platforms, with lower technical and development costs, higher deployment and interfacing efficiency, and faster expansion of public chains it serves
- New public chains tend to cooperate with the cross-chain bridge with the most supported public chains, the largest amount of funding (good cross-chain depth), the largest volume of users and the highest popularity, strengthening Anyswap’s competitive advantage and giving it a network effect
However, this report argued that only the third advantage is Anyswap’s real moat at the moment, making it harder for Anyswap’s successors to catch up.
Is the Medium- to Long-term Investment Logic Clear? Is It in Line with the General Trend of the Industry?
The asset cross-chain bridge business is based on the maintenance or even expansion of the multi-chain landscape. Despite the rapid development of new public chains in 2021, most of the projects with commercial innovation and demonstration effect are mostly on Ethereum (except for the chain tour ). As Ethereum receives a performance boost, new public chains will no longer boast an advantage. Hence, it remains to be seen whether the multi-chain pattern can be maintained.
What are the Main Variable Factors in the Operation of the Project? Are Such Factors Easy to Quantify and Measure?
The main variable factor is whether the cross-chain demand for these public chains has been activated after a large number of public chains have been deployed to generate actual cross-chain business.
Currently, Anyswap only discloses the total cross-chain amount, number of transfers and active addresses, but not the business data of individual public chains. Therefore, this report can only provide a global view of the project from an aggregate perspective.
What is the Management and Governance Approach? How About the DAO?
The project is not yet open for node campaigning, nor has it initiated a governance mechanism for the community.
Valuation
Anyswap has turned on the fee repurchase and destruction mechanism and disclosed its daily, weekly and monthly fee income, so it is measured from the PS/PE perspective. Here’s how it works:
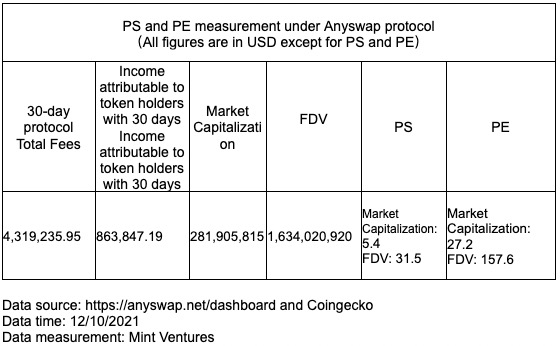
PS and PE were measured in the table above based on Anyswap’s circulating market cap and fully diluted market cap (FDV). The two figures were vastly different since the Any tokens that were released only accounted for about 20% of the total whereas the other 80% were in a locked position. But which data is actually more informative?
In this report, Anyswap’s earnings multiple calculated on circulating market cap is more informative for the following reasons.
- Since February 2021, Anyswap has suspended the addition of tokens to circulation and has not announced plans for token circulation for the time being.
- Unlike most DeFi protocols, Anyswap does not initiate any liquidity mining programs. Its token rewards in occasional events come from team shares or community funds, which are already counted in the circulating market cap and therefore do not result in an expansion of the circulating token volume.
Anyswap, which does not rely on liquidity mining, has no direct business motivation to unlock Any quickly
- The remaining 80% of tokens have the potential to be destroyed
Therefore, Anyswap will probably maintain the current number of tokens in circulation in the medium term, so it is relatively more informative to calculate its PE and PS using the market capitalization in circulation.
Anyswap currently has a reference PE of 27.2 and a PS of 5.4, but PE may be more informative for coin holders, as only 20% of Anyswap’s current protocol revenue is related to coin holders.
Mainstream DeFi projects have the following PE profile.
Data source: Token Terminal
Curve boasts the highest PE at 146x (thanks to its subtle lock-in and participant gaming mechanism), followed by two major lending protocols, Aave and Compound, at 70x and 56x respectively, while most of the other protocols have their PE values in the 6x-20x range.
In the DeFi sector, Anyswap is moderate.
Since there are very complex factors behind PE, including the sub-track situation of each project, project mechanism, and future development, the comparison can only be used as a rough reference, and does not give strong explanation in actual high or low valuations.
Disclaimer: None of the contents of this report should be taken as investment advice.
References
Building Networks of Cryptonetworks:
https://medium.com/1kxnetwork/blockchain-bridges-5db6afac44f8
What is this cross-chain stuff?
https://andrecronje.medium.com/what-is-this-cross-chain-stuff-3528540423e1
Multichain dapp guide, standards, and best practices:
https://andrecronje.medium.com/multichain-dapp-guide-standards-and-best-practices-8fabe2672c60
Official documentation and data:
Documentation: https://anyswap-faq.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
Announcement: https://anyswap.medium.com/
Data:
Industry Data: